CUVIS-joint
is a cutting-edge surgical robot system that improves the completion of artificial joint surgery with optimal surgical planning and precise cutting.
With optimal tracking sensors and self-developed surgical planning CUVIS-joint helps patients that are in need of artificial knee surgery.
Why CUVIS-joint is good?
-
Point. 01
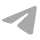
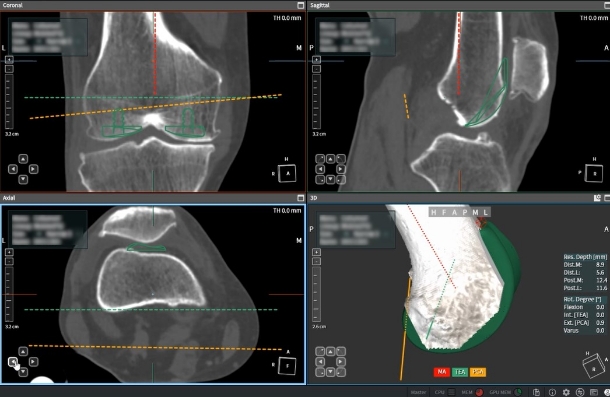
Surgical Planning & Execution Based on 3D CT Analysis
Surgical Planning & Execution Based on 3D CT Analysis
Precisely analyzes the patient's bone morphology based on pre-operative 3D CT images and accurately predicts femoral (98.9%) and tibial (100%) implant sizes.1
Precise Bone Resection
The robotic arm performs precise bone resection within a 1mm error margin (98% rate) within the planned range.1
Sophisticated Angle Control
Maintains the cutting angle error (RMS) below 1 degree, ensuring that simulation results are perfectly reproduced in the actual operating room.2
-
Point. 02
Optimal Soft Tissue Balance and Alignment
Real-time Gap Balancing
Checks and adjusts the gap balancing of the medial and lateral knee in real-time during surgery to support achieving ideal balance.3 4
Functional Alignment
Goes beyond simply straightening the bone by identifying the optimal rotational alignment reflecting the patient's specific rotational axes (TEA, PCA).5 6
Joint Line Restoration & Soft Tissue Preservation
Restores the anatomical position by maintaining pre- to post-operative joint line height changes at an average level of 1.65mm, and reduces the frequency of unnecessary soft tissue releases.7 8
-
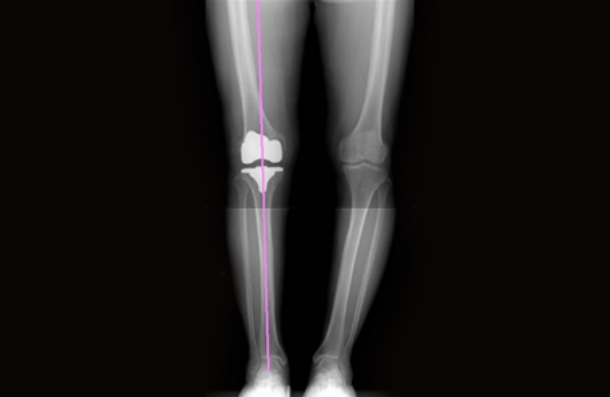
Point. 03
Safety and Versatility
Surgical Safety
Recorded 0 cases of major surgical complications, such as nerve and blood vessel damage, in a large-scale study of 500 cases at a single institution.9 Additionally, the safety of pin insertion sites is secured through methods such as intra-incisional pin fixation.10 11
Wide Range of Application
Stable surgery is possible without complications even in morbidly obese patients where surgical field visibility is difficult,12 and accurate correction angles are achieved even in patients with high-difficulty deformities such as severe valgus knees.13
-

Point. 04
Pain Reduction and Functional Recovery
Initial Pain Relief
Reduces tissue damage through precise resection, aiding in the reduction of pain scores (VAS) and analgesic consumption in the early post-operative period (Days 1-2). 14
Verified Functional Recovery
Demonstrated excellent clinical results in OKS(Oxford Knee Score) and FJS(Forgotten Joint Score) 1 year after surgery.15 16
References
-
1
Adkar N, et al. Correlation Between Planned and Executed Bone Cuts Using Robotics in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Study of 500 Patients. Indian Journal of Orthopaedics. 2024.
-
2
Patil S, Wankhede C. Achieving Accuracy and Gap Balancing with Fully Autonomous Cuvis Joint Robot Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Single-Center, Non-Randomized Retrospective Study. Journal of Orthopaedic Reports. 2024.
-
3
Bhat AK, et al. Gap Balancing Technique With Functional Alignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty Using the Cuvis Joint Robotic System: Surgical Technique and Functional Outcome. Cureus. 2025.
-
4
Jung WH, et al. Evaluating the Accuracy of Cuvis™ Robot Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Using Offset Type Tensor System in Ligament Gap Balancing. Journal of Clinical Orthopaedics and Trauma. 2025.
-
5
Londhe SB, et al. Evaluation of the External Rotation of the Femur Component in Functionally Aligned Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty. Cureus. 2024.
-
6
Murugesan HK, et al. Assessment of Average Femoral Component Rotation for Balancing Functionally Aligned Total Knee Replacement in Varus Deformity: Robotic Image Guidance Study. Journal of Orthopaedics. 2024.
-
7
Londhe SB, et al. Minimized Soft Tissue Release in Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Review of 100 Cases. Cureus. 2024.
-
8
Bhor P, et al. Is Native Joint Line More Accurately Restored with Robotic Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty than with Conventional Instruments? Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports. 2025.
-
9
Chandrashekar P, et al. Intra-Operative Safety of an Autonomous Robotic System for Total Knee Replacement: A Review of 500 Cases in India. Indian Journal of Orthopaedics. 2023.
-
10
Mehta C, et al. Our Initial Experience of First 50 Cases of Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty. Journal of Clinical Orthopaedics. 2024.
-
11
Bhattacharjee S, et al. Evolving Techniques in Active Robotic Arm-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Study of Pin Placement Strategies. Journal of Robotic Surgery. 2025.
-
12
Bhattacharjee SK, et al. Functional Outcome in Obese Patients Undergoing Image-Based Cruciate Retaining Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Using the Subvastus Approach: A Short-Term Study. Cureus. 2024.
-
13
Rajashekhar KT, et al. Achieving Accuracy and Gap Balancing in Fully Autonomous Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty with Functional Alignment in Valgus Knee Deformity. Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports. 2025.
-
14
Londhe SB, et al. Comparative Analysis of the Immediate Post-operative Outcomes between Conventional and Fully Automatic Robotic-assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty. Journal of Clinical Orthopaedics. 2023.
-
15
Han SH, et al. Clinical Benefit of Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty over Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty When Using Mobile-Bearing Implants. Medicina. 2024.
-
16
Bhattacharjee S, et al. Comparative Analysis of Joint Awareness and Functional Outcomes in Robotic vs Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Study with 1-year Follow-up. Research Article. 2024.
※ These products are medical robots. Please check the caution and instructions before use.
※ Disclaimer The advantages and safety data of robotic surgery presented herein are summarized based on multiple clinical research papers conducted using CUVIS-joint. This content summarizes clinical statistics and researchers' analyses; it does not guarantee the same results for all patients. We recommend consulting with a specialist for an accurate diagnosis.