-

Step. 01
Patient Selection
Patients can decide upon robotic artificial joint surgery after consulting the doctor.
-
Step. 02
CT Scan
CT scanning.
-
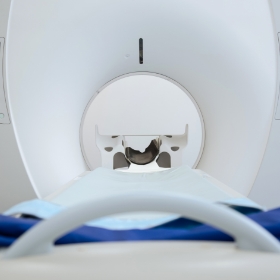
Step. 03
Pre-Surgical Planning
The scanned CT image is converted into a 3D image in Planner.
The doctor diagnoses the patient’s condition and makes a surgical plan using the converted image.
TKA
-
FMA, TMA setting
Mechanical axis setting between Femur and Tibia
-
Rotation
Image based External Rotation setting of patient’s bone
-
Implant Selection
-
Virtual Surgery
A virtual check of postoperative alignment of patient’s leg (Femur/Tibia)
* FMA : Femoral Mechanical Axis / TMA : Tibia Mechanical Axis
THA
-
Femoral Head Setting
Position/size setting of Femur Head
-
Femur Cavity Adjustment & Alignment
Alignment for implant insertion
-
Implantation
Mechanical axis setting between Femur and Tibia
-
Synthetic X-Ray
A check of implant insertion state after virtual X-ray surgery
* FMA : Femoral Mechanical Axis / TMA : Tibia Mechanical Axis
-
-
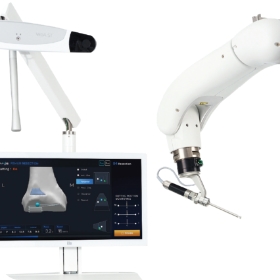
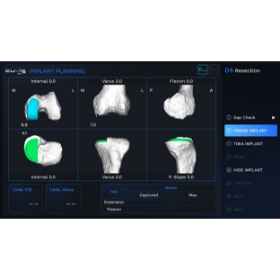
Step. 04
Surgical Implementation
The patient is connected to the robot and fixed to keep still for surgery.
If the patient and the robot are connected, the doctor performs the registration process to verify if the 3D image of the patient matches the original surgery site of the patient.
When the registration is completed, the robot reviews the data finally and cuts the bone precisely in the size, position, angle, and direction of the implant decided in the surgical planning state.
-
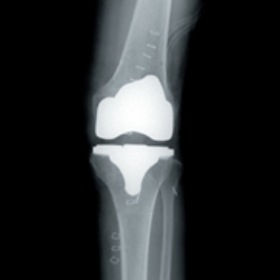
Step. 05
Implant placement
Insert and fix the implant decided and finished the surgery.